The e-CVT uses a planetary gear system to change the transmission ratio between the engine and the wheels, instead of a belt and pulley like a conventional CVT.

The gearbox on a car is used to change the transmission ratio from the engine to the wheels, in order to adjust the engine's traction and the wheel speed. In low gears, the traction is strong but the car cannot reach high speed. On the contrary, in high gears, the car can run fast but the traction is reduced. In manual and automatic transmission cars, the transmission ratio is fixed at each gear.
In a CVT, which stands for Continuously Variable Transmission, the gear ratio can be changed (varied) theoretically infinitely. CVT uses belts and pulleys with variable radii to change the gear ratio.
The advantage is that the gear ratio changes continuously, making the car smoother, but the disadvantage that many people are afraid of is the durability of the belt. Therefore, CVT is still a concept that brings many concerns to users, even with hybrid cars.
Hybrid cars also use a CVT, but it is an e-CVT, first applied on the Toyota Prius. Although the name is only different in the prefix, the e-CVT has a completely different structure compared to a conventional CVT.
Instead of using the belt and pulley system of the CVT, the e-CVT uses a planetary gearset to change the gear ratio, and allows the car to charge the battery while the gasoline engine is running. Therefore, the gear ratio of hybrid cars using e-CVT can change indefinitely, similar to cars equipped with CVT.
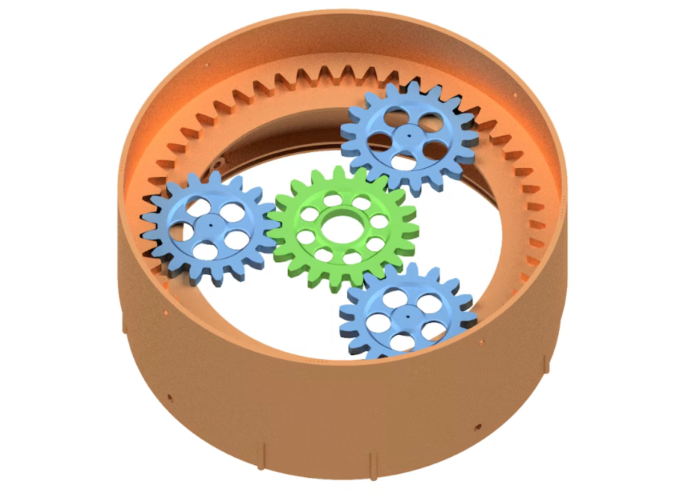
On a planetary gear, the center gear is called the "sun" gear, surrounded by rotating "planet" gears, and there is a ring gear that encircles the entire planet.
In it, the internal combustion engine is connected to the "planet", the wheels and the main motor/generator are connected to the belt, and the auxiliary motor/generator (smaller in size than the main generator) is used to power the electric motor, which is connected to the "sun". All these gears can rotate, so it is possible to distribute the speed and traction between the "sun" gear and the belt.
For example, if the "planet" rotates at 100% speed and the "sun" stops, the belt will rotate at 100%. If the belt stops, the sun will rotate at 100%. If neither the "sun" nor the belt is stopped, the "sun" will rotate at 50% speed, the belt will rotate at 50%. By regulating the power transmitted through the electric motor or internal combustion engine, the vehicle can create a gear ratio to suit the operating condition of the vehicle.
With current technology, many manufacturers use different types of e-CVTs, but they are not belt-driven like conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. Therefore, hybrid vehicles using e-CVTs will not have the problems that many users worry about with traditional CVTs, such as belt wear or difficulty in repairing when damaged.
However, even with traditional CVTs, if users use them as recommended and perform regular maintenance, the failure rate is very small.
HA (synthetic)