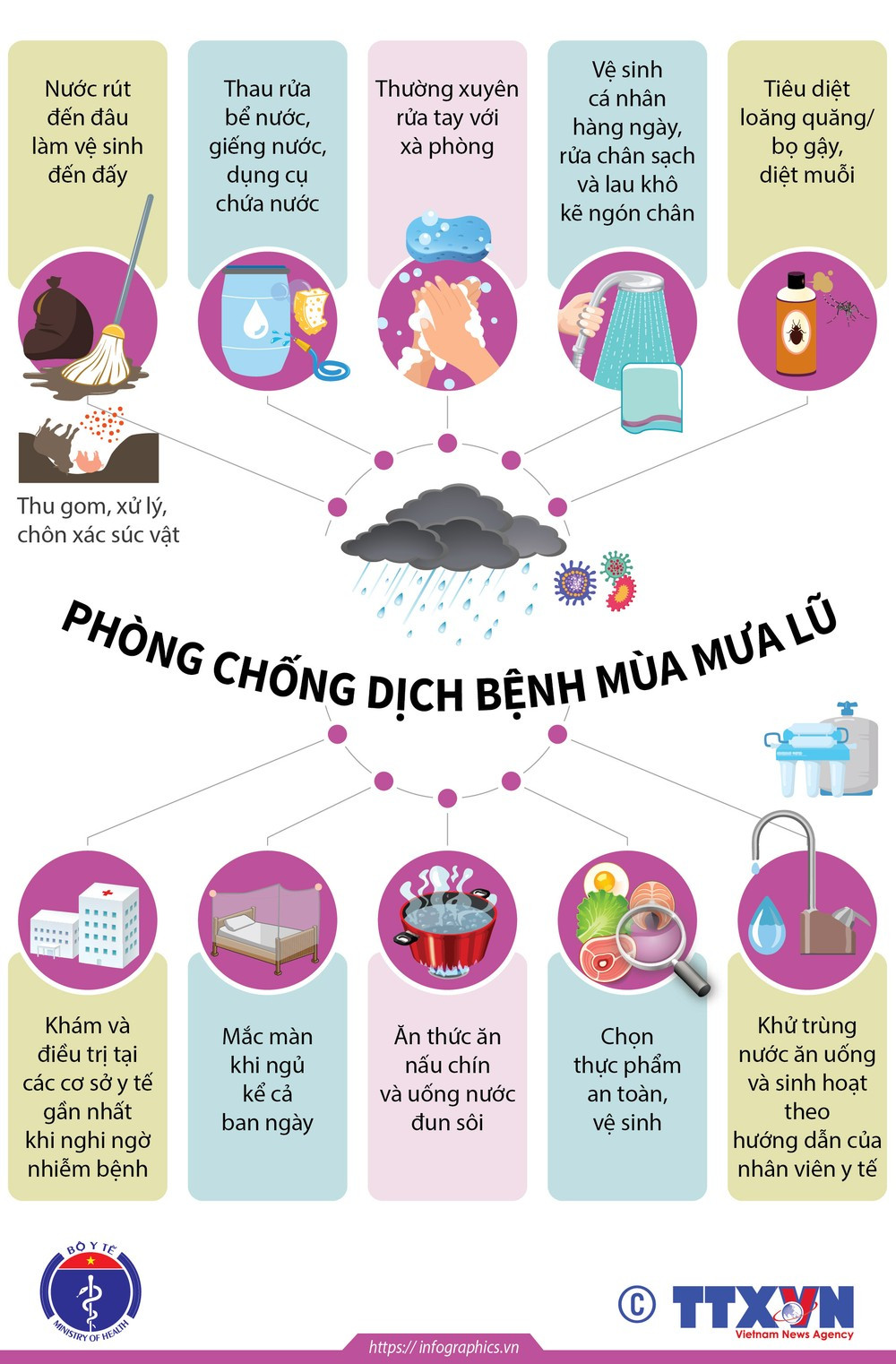
The Department of Preventive Medicine recommends that people proactively prevent infectious diseases that often occur after floods, including diarrhea, pink eye, respiratory infections, flu, dengue fever, and skin diseases.
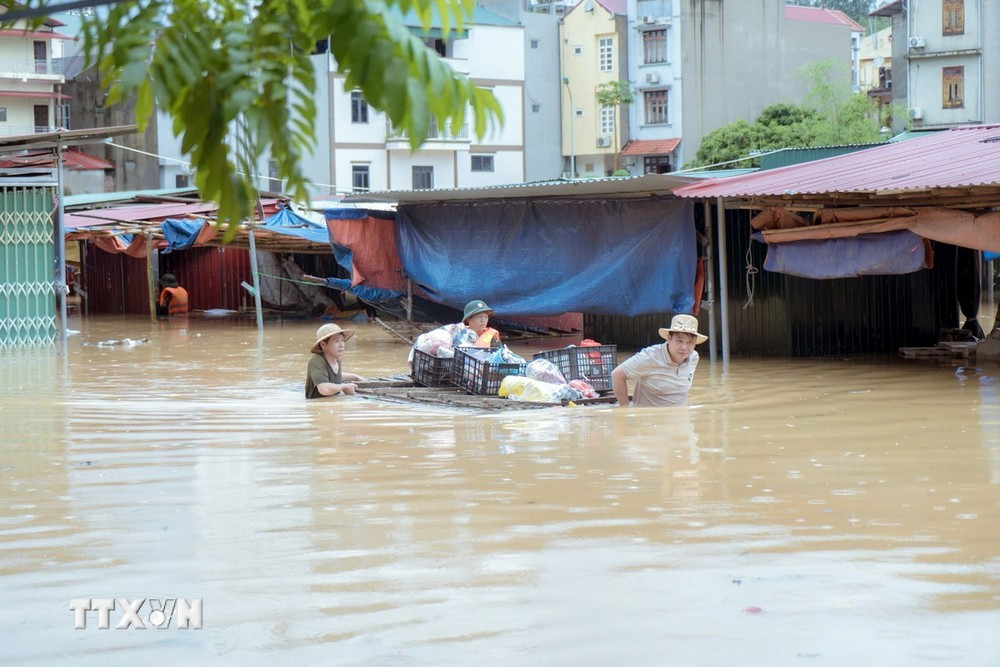

During and after storms and floods, many microorganisms, dust, garbage, waste, etc. will flow with the water to many places, causing environmental pollution and potentially causing many epidemic risks.
Furthermore, rain and flooding are favorable conditions for bacteria, viruses and disease vectors to grow and cause diseases in humans.
Common diseases during the rainy season are acute diarrhea, respiratory diseases, eye diseases, skin diseases, dengue fever, especially the risk of COVID-19 epidemic in storms, floods, and natural disasters.
The Department of Preventive Medicine recommends that people proactively prevent infectious diseases that often occur after floods, including diarrhea, pink eye, respiratory infections, and flu.
The Department of Preventive Medicine recommends that people ensure safe and hygienic food selection and preparation, eat cooked food and boiled water.
Wash your hands regularly with soap before and after preparing food, before eating and after using the toilet.
Practice daily personal hygiene, wash feet and dry between toes after contact with flood water or contaminated water.

Kill larvae/wigglers, kill mosquitoes by covering tanks, water containers, putting fish in large water containers, removing waste such as bottles, jars, car tires... or natural water holes to prevent mosquitoes from laying eggs. Use mosquito nets when sleeping even during the day.
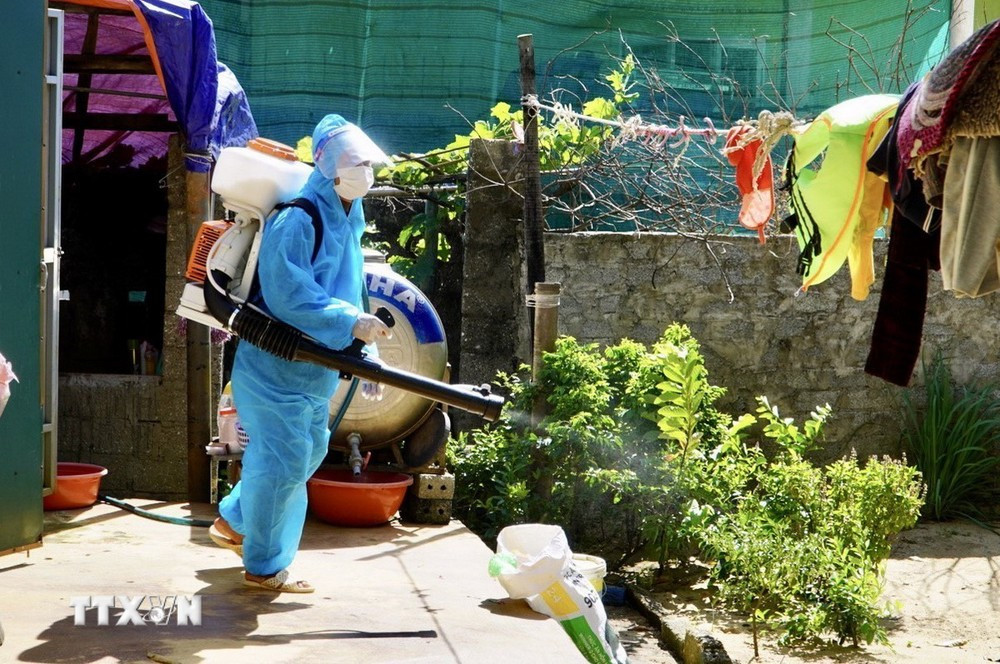
Clean water tanks, wells, water containers and use chemicals to disinfect drinking water and domestic water according to the instructions of medical staff.
Clean up as water recedes, collect, treat and bury animal carcasses according to the instructions of medical staff.
When there are signs of suspected infection, you should go to the nearest medical facility for examination and treatment.
Gastrointestinal infections
Common diseases:Diarrhea caused by E. coli bacteria, cholera, dysentery, typhoid, hepatitis A. The disease appears due to the use of unsanitary water sources and contaminated food.
Prevention:
Ensure drinking water treatment, environmental sanitation and personal hygiene. Implement the principle of "Eat cooked food, drink boiled water", ensure food safety and hygiene.
Ensure enough clean water for eating and drinking. Wash hands with soap before eating and after using the toilet.
Properly handle manure, waste, garbage and dead animals.
Take or inject vaccines when indicated for diseases for which vaccines are available.
Respiratory disease
Common diseases:Cold, flu, sore throat, respiratory tract infection
Prevention:
Keep warm in cold weather, especially for children and the elderly.
Limit contact with people showing signs of flu or respiratory infections.
Ensure adequate nutrition.
Timely diagnosis and treatment to limit complications and death.
Eye disease
Common diseases: Pink eye, blepharitis, lacrimal gland inflammation.
Prevention:
Do not wash your face or bathe with dirty water.
Do not let children bathe or play in dirty water.
Wash hands with soap and clean water.
Do not share towels and wash basins with people who have pink eye.
Apply eye drops (Chloramphenicol 0.4% or Argirol 1%) to all persons at risk of exposure to contaminated water.
Pay attention to kill flies because flies transmit pink eye from sick people to healthy people.
Skin disease
Common diseases: Foot and hand fungus, folliculitis, ringworm, pityriasis versicolor, scabies, acne.
Prevention:
Do not bathe or wash clothes with dirty water. If you do not have disinfected well water, you must add alum or filter the water with sand.
Do not wear wet clothes.
Do not swim, bathe or play in flooded water because the water is very dirty. In addition to causing skin diseases, it also causes digestive diseases due to swallowing dirty water.
Avoid wading in stagnant dirty water. If you must wade in dirty water, immediately rinse with clean water and dry, especially between fingers and toes.
Mosquito-borne diseases
Common diseases: Dengue fever
Prevention:
Sleep under a mosquito net and wear long clothes to prevent mosquito bites even during the day.
Kill mosquito larvae, treat water containers to prevent mosquitoes from laying eggs.
Spraying chemicals to kill mosquitoes in high-risk areas or areas with dengue fever outbreaks
If you have a fever, go to a medical facility immediately for examination and treatment advice. Do not self-treat at home.
TB (according to Vietnam+)