Since the beginning of the year, the country has recorded about 9,000 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease, with 3 deaths. In Hai Duong, the number of children with this disease has tended to increase in the past 2 months.
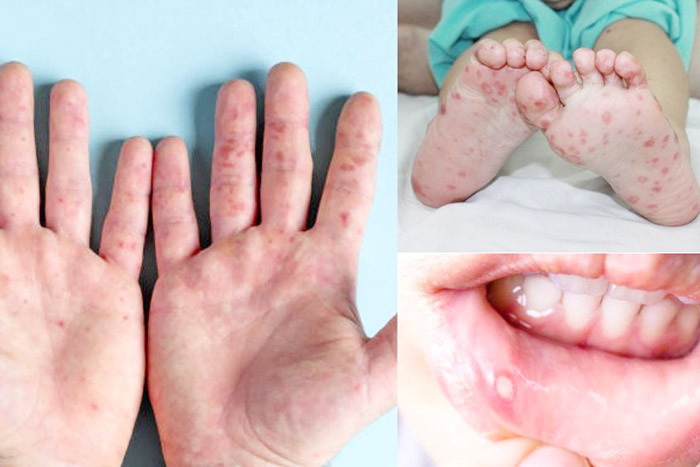
Typical symptoms of children with hand, foot and mouth disease (internet photo)
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an infectious disease caused by Coxsackievirus and Enterovirus 71 (EV71). The disease occurs year-round, mainly in children under 5 years old, less common in older children. The following notes will help parents know how to care for and prevent children from getting hand, foot and mouth disease.
Transmission of hand, foot and mouth disease
The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease is spread through contact. Children are susceptible to infection if they come into contact with nose and throat secretions, saliva, fluid from blisters, stool or vomit of an infected child.
Typical symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease
The incubation period is from 3-7 days; the onset period is from 1-2 days with symptoms such as mild fever, fussiness, sore throat, loss of appetite, diarrhea several times/day; the full-blown period is from 3-10 days with typical symptoms of the disease such as mouth ulcers (red ulcers or blisters on the oral mucosa, gums, tongue causing mouth pain, refusing to breastfeed, refusing to eat, increased salivation, drooling and blisters (appearing on the palms, soles, knees, buttocks, lasting for about 7 days, then leaving dark spots); the remission period is from 3-5 days, after which the child recovers completely if there are no complications.
Hand, foot and mouth disease causes many neurological complications (encephalitis, meningitis); cardiovascular and respiratory complications (myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema, hypertension, heart failure, circulatory collapse) if not monitored and treated promptly.
How to care for children with hand, foot and mouth disease
Isolate by contact, limit children from going out to avoid infecting other children; combine antibiotics and antipyretics as directed by medical staff; wash hands before and after each time taking care of children; clean the mouth and apply medicine to the child's mouth as directed by the doctor (usually clean 30 minutes before feeding the child); feed the child cold, soft, liquid, easy-to-digest foods such as porridge, milk and divide into many small meals; keep the skin clean, use methylene blue to dab on blisters; wear soft, loose, sweat-absorbent clothes; change clothes and bathe the child daily with warm water.
Monitor the child's condition, detect early warning signs and severe signs for timely treatment: rapid pulse, limb tremors, unsteady gait (if the child can walk); startle >2 times/30 minutes.
Disease prevention
Adults should wash their hands with soap before caring for children and after contact with children's waste. Wash toys and mop floors with appropriate disinfectants. Do not let sick children go to daycare, crowded places or come into contact with other children.
When children with hand, foot and mouth disease have unusual symptoms, parents need to quickly take them to the nearest medical facility for timely examination and treatment.
MT(synthetic)