Humanity has long dreamed of exploring the universe, and more than 65 years ago, humans achieved that dream for the first time.
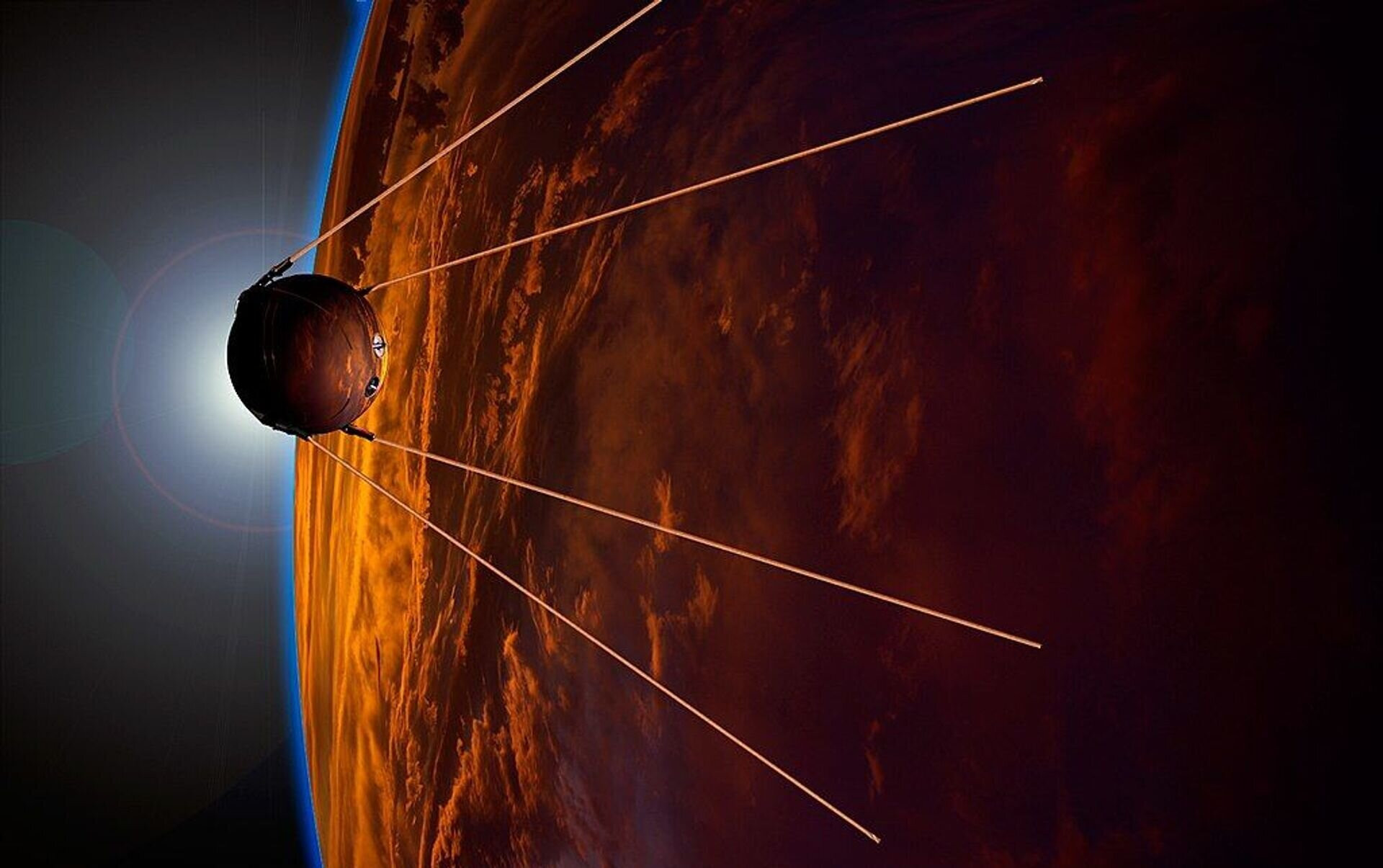

Sputnik 1 was the world's first man-made object to orbit the Earth. It was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Soviet Union and entered low Earth orbit on October 4, 1957. Sputnik orbited the Earth 1,440 times, remaining in low Earth orbit until January 4, 1958, when it burned up upon re-entry into the Earth's atmosphere. Sputnik 1 essentially helped humanity learn about the properties of the Earth's atmosphere.
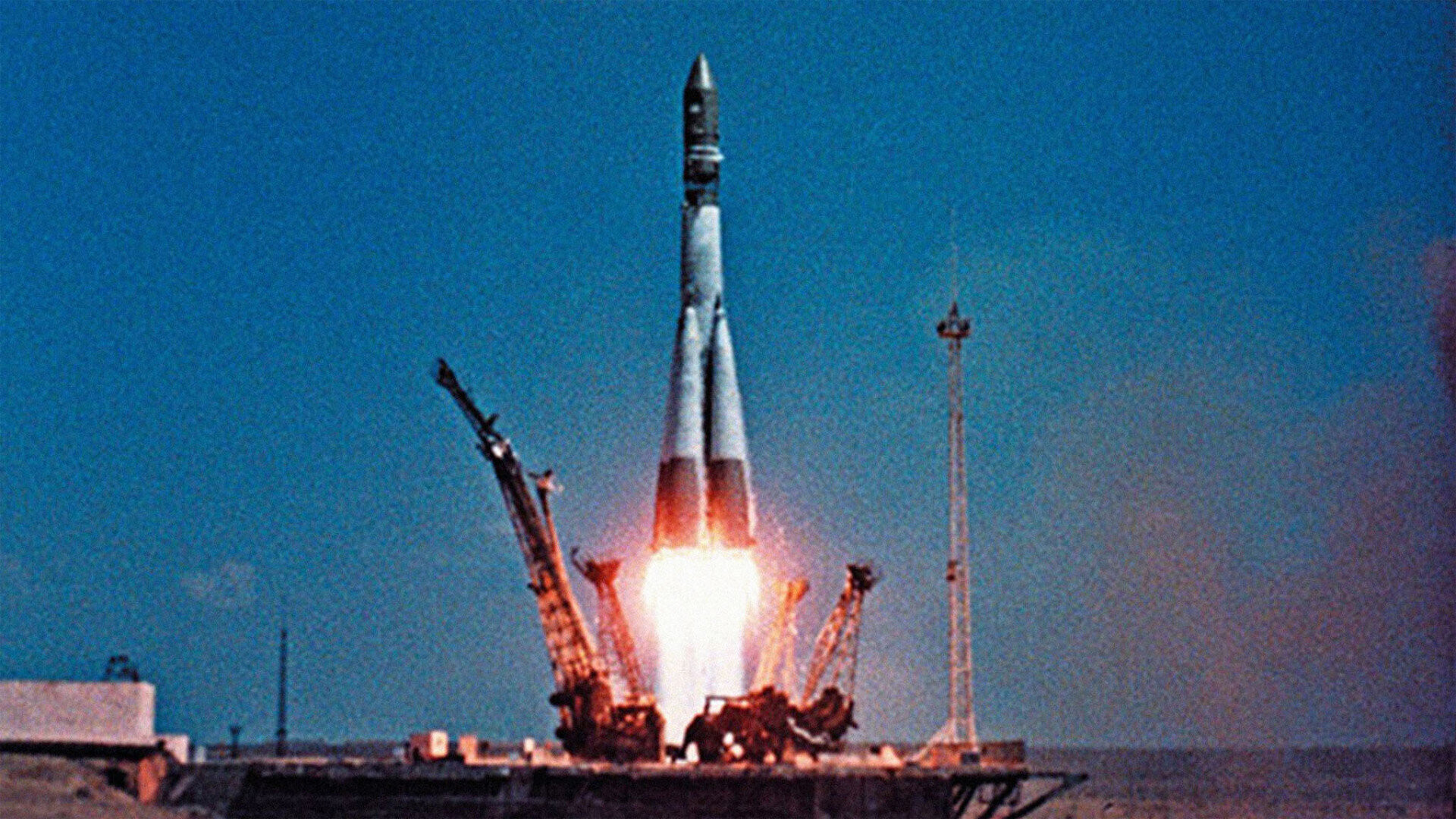

On April 12, 1961, Yuri Gagarin launched into space, becoming the first human to fly into space. He launched the Vostok 1 spacecraft mission, orbiting the Earth once for 108 minutes, before he and his spacecraft safely parachuted back to Earth.
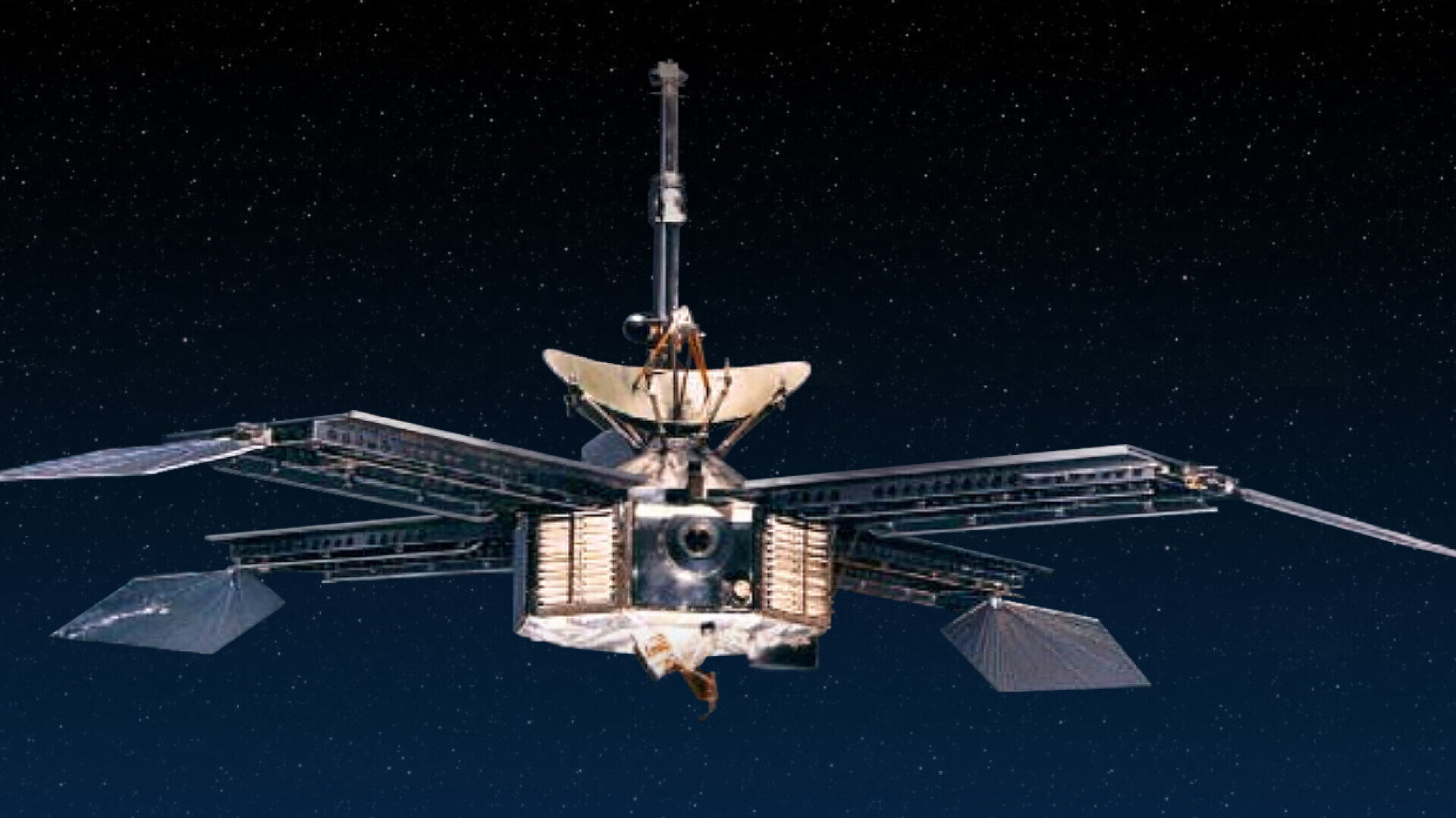

On July 15, 1965, NASA’s Mariner 4 spacecraft transmitted the first images of Mars. The spacecraft stayed in orbit around the Sun for about three years, exceeding its scheduled eight-month mission time and helping to shed new light on the Martian solar wind.
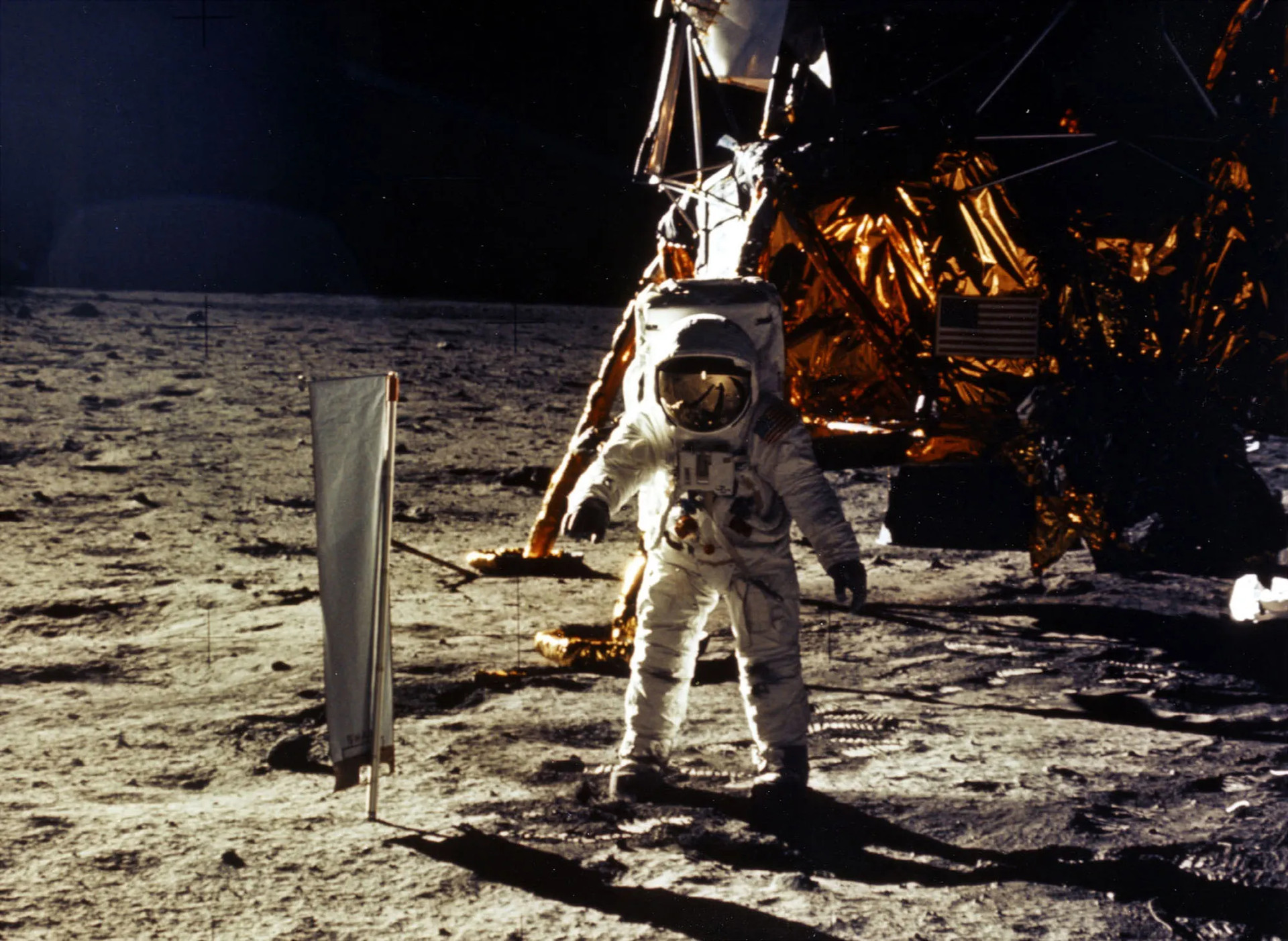

On July 21, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first man to set foot on the Moon aboard the Apollo 11 mission. About 20 minutes after Armstrong stepped onto the lunar surface, he was joined by Lunar Module Pilot Buzz Aldrin. The two spent about three hours conducting experiments and collecting samples.
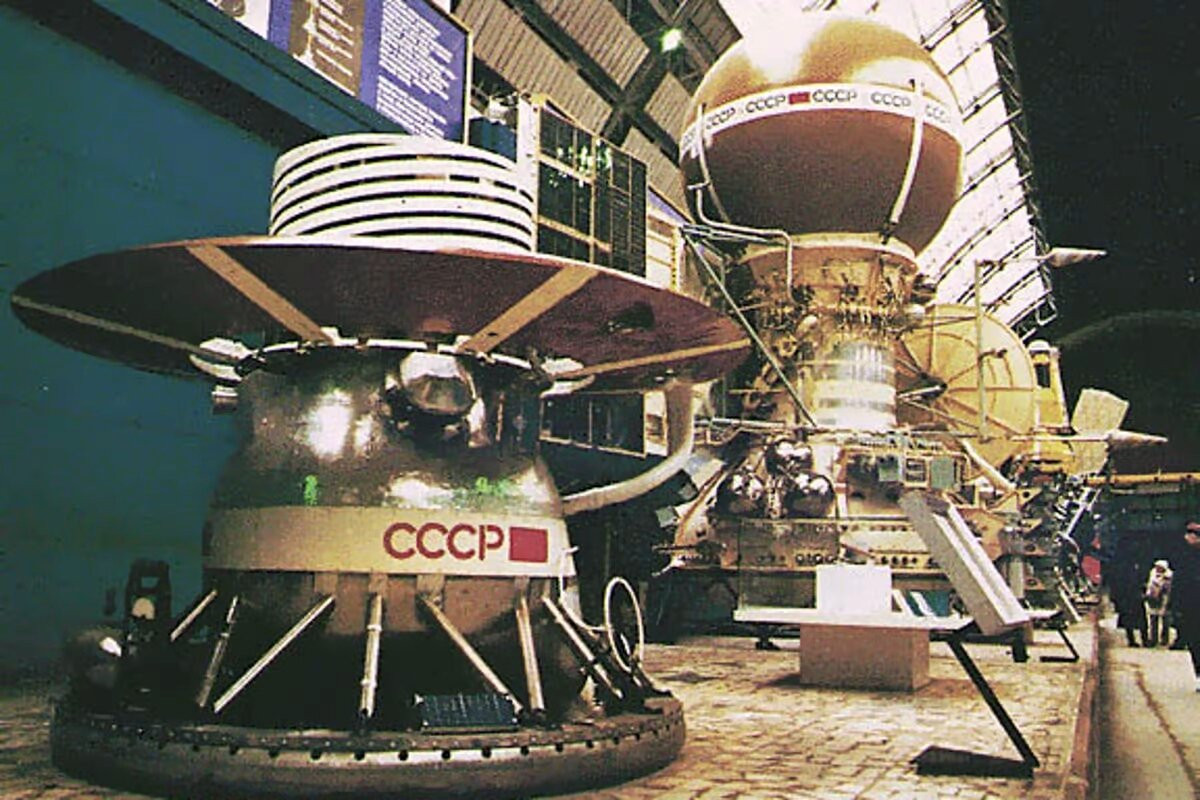

On December 15, 1970, the Soviet Venera 7 spacecraft landed on the surface of Venus. Although the spacecraft's systems were destroyed by the extreme heat and pressure of the Venusian surface within an hour, it collected a wealth of data about the neighboring planet.
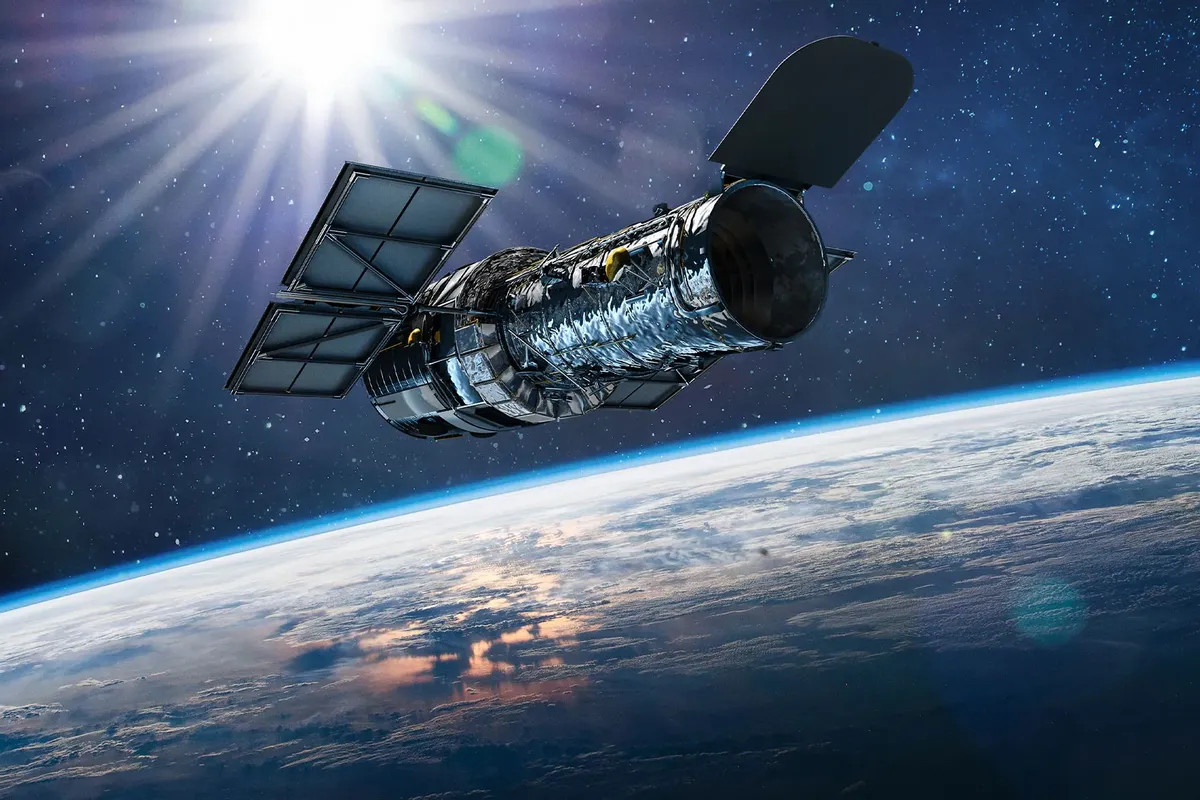

The Hubble Space Telescope orbited Earth for more than 30 years, launched on April 24, 1990. Over three decades, Hubble made more than 1.5 million observations, creating a treasure trove of data that led to the publication of more than 18,000 papers by Earth scientists.scienceon topics ranging from dark energy to black holes to gamma ray bursts.
NASA's Mars Pathfinder robotic spacecraft touched down on the surface of Mars on July 4, 1997. As it touched down on the surface of the Red Planet, it deployed several airbags to stabilize itself during its descent. Once there, the spacecraft explored the Ares Vallis region of the Red Planet, beginning to analyze its atmosphere, climate, and geology. It also collected evidence that Mars once had flowing water on its surface.
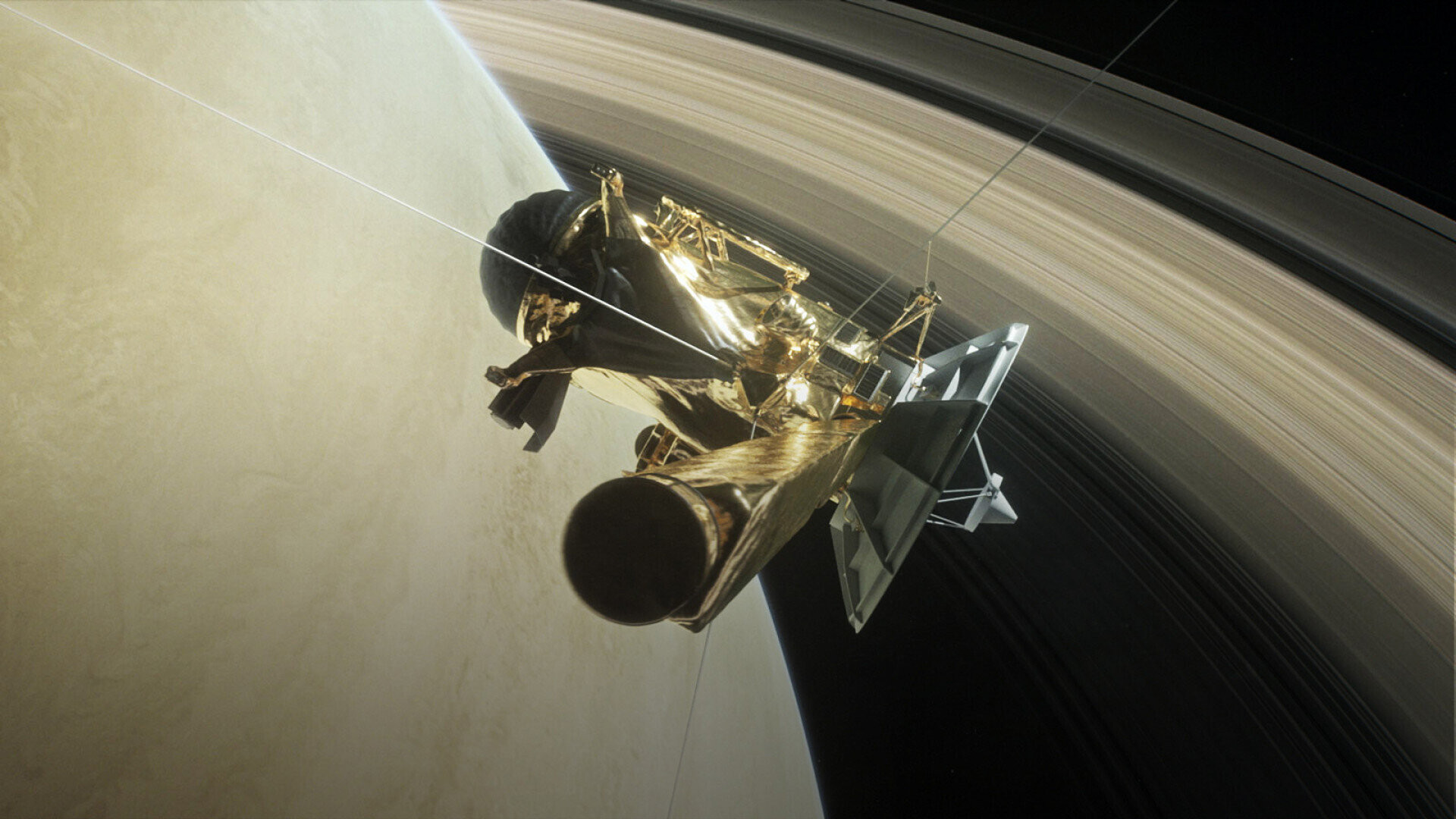

The Cassini Saturn probe is a collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Italian Space Agency. Cassini collected data about Jupiter during a flyby before flying to Saturn. While there, Cassini collected a large amount of data and images from the planet’s rings. In all, Cassini spent 20 years in space before it crashed into Saturn on September 15, 2017.
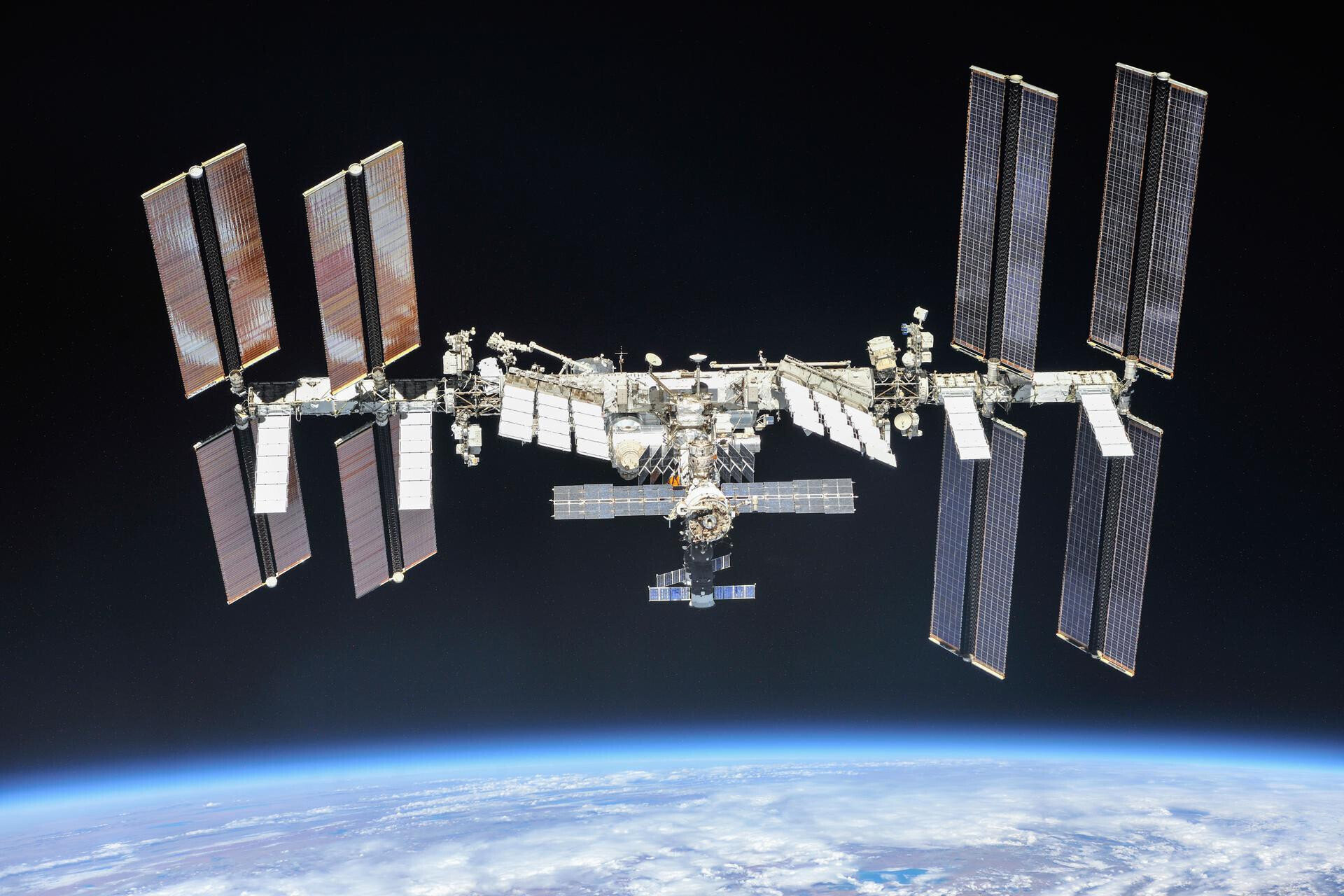

The International Space Station (ISS) ushered in an era of unprecedented global collaboration in space exploration. It became operational in November 2000. Since then, the station has been home to many international astronauts and cosmonauts.
The James Webb Space Telescope has been operational for just over a year now. It has already changed our understanding of the universe. Before it moved to its current location at Lagrange Point 2, about a million miles from Earth, James Webb was billed as a major astronomical instrument that would usher humanity into a new era of astronomy. And sure enough, just a week after it began observing, it has revealed an image of the oldest, most distant galaxy ever observed, the 13.5-billion-year-old GLASS-z13.