Electric car batteries are actually quite durable, with the commonly used lithium-ion type capable of lasting at least a decade before needing to be replaced.
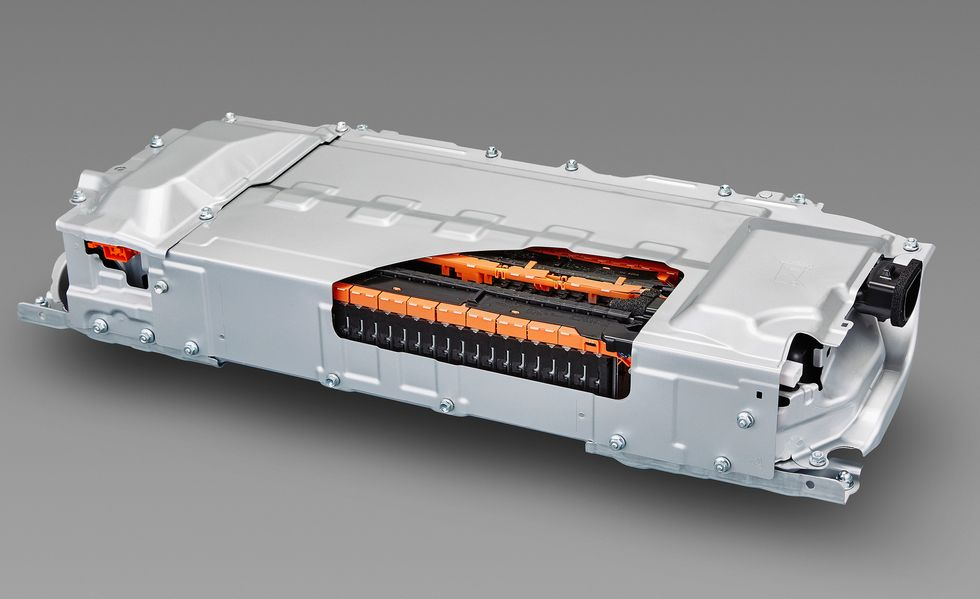
Compared to internal combustion engine vehicles, electric vehicles have fewer moving parts, and the use of regenerative braking reduces the frequency of replacement of brake pads and brake discs, requiring much less maintenance. However, what consumers worry about is replacing electric vehicle batteries in the event of a failure.
Most electric vehicles use lithium-ion batteries, and the infrastructure today caters to them. They will remain the dominant battery type in the electric vehicle market for the foreseeable future.
Lithium-ion batteries have the following benefits
- Higher energy density than conventional lead-acid batteries used in internal combustion engine vehicles, or nickel-metal hydride batteries found in some hybrid vehicles such as the Toyota Land Cruiser or 4Runner.
- Lower self-discharge than other batteries, only losing 1 to 2% per month (if weather conditions are not too harsh).
- No periodic complete discharge required, nor electrolytic maintenance required.
- Provides stable voltage even when battery capacity decreases.
The easiest way to gauge the expected lifespan of a battery pack is to look at the manufacturer's warranty information. All manufacturers today offer at least an 8-year, or 100,000-mile (160,000 km) warranty on their battery packs.
Tesla, for example, offers an eight-year battery warranty, and depending on the range and type of vehicle, the warranty ranges from 100,000 to 150,000 miles (160,000 to 240,000 km). Over time, each charge cycle reduces the capacity of a lithium-ion battery pack. Tesla says its vehicle batteries must maintain at least 70% of their capacity during the warranty period. If the capacity falls below this threshold, the battery will be replaced free of charge.
Hyundai and Kia offer similar warranties for their electric vehicles.
The U.S. Department of Energy predicts that current electric vehicle batteries will last significantly longer than their warranty period, with a useful life of 12 to 15 years if used in a mild environment. If used regularly in harsh conditions, that number is still 8-12 years.
Electric vehicles sold in the United States, for example, must adhere to the same safety standards as all other passenger vehicles. Additionally, EV battery packs must be housed in sealed enclosures and must be able to handle testing conditions involving overload, extreme temperatures, explosions, crashes, water immersion, vibrations, and short circuits, according to the Department of Energy. They must also use “high-voltage insulated wiring” and must be able to shut down the electrical system in the event of a crash or short circuit.
Overall, electric cars are much less likely to catch fire than internal combustion engine cars. A recent study from Sweden, using data from US insurance companies, found that for every 100,000 cars sold, there were 1,530 fires reported for gasoline-powered cars and 3,475 fires reported for hybrids. Electric cars? Just 25.
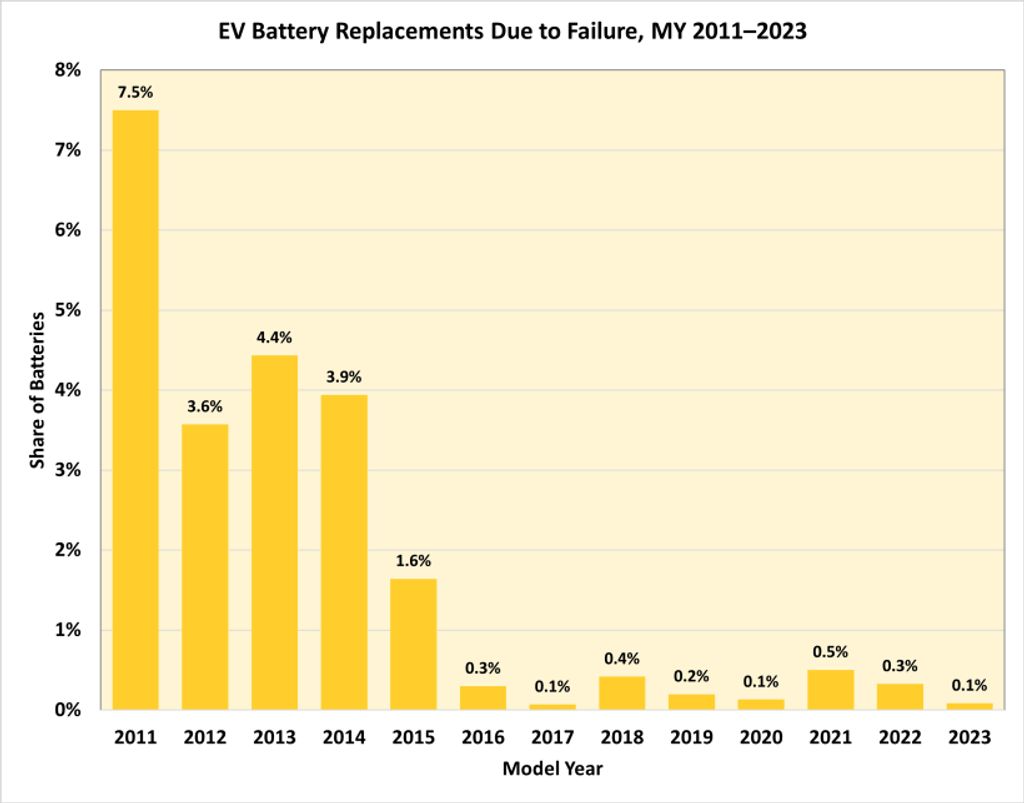
According to a recent study by battery health startup Recurrent, cited by the U.S. Department of Energy, the number of electric vehicle batteries replaced due to failure from 2016-2023 models has dropped significantly compared to 2011-2015 models. The figure is based on a survey of 15,000 vehicles.
The replacement rate was 0.5 percent for the 2016 model, but most later models have dropped to 0.1 to 0.3 percent. Most issues are covered by the manufacturer's warranty, the report said. These improvements come from learning and improving technology, from active liquid cooling to new battery thermal management strategies to new battery chemistries.
TH (according to VTC News)