The news of 3 deaths from hand, foot and mouth disease and nearly 9,000 cases has made many families with young children very worried.
In the hot summer, what makes parents wonder is whether children can get sick when swimming?
Hand, foot and mouth disease can cause dangerous complications such as encephalitis, myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema... leading to death if not detected early, monitored and treated promptly. Therefore, early detection of children with hand, foot and mouth disease is extremely important.
Transmission of hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by viruses in the Enterovirus group. Enterovirus (EV) includes the groups: Poliovirus, Coxsackie and Echovirus. Because there are many groups of viruses, each time the human body is infected, it only produces antibodies to a certain type of virus. That means children can get hand, foot and mouth disease many times if infected with another virus in the Enterovirus group.
Viral diseases are easily spread by viruses in body fluids from infected children, through contact or through the environment entering the bodies of healthy children.
The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease can spread very quickly, transmitted directly from person to person, through the mouth, through secretions from the nose, mouth, feces or saliva of sick children.
Infected people are able to spread the virus during the first week (incubation period). However, the period of infection can last for several weeks, because the virus still exists in large quantities in the patient's stool and saliva.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by a virus in the Enterovirus group.
The main transmission routes of the virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease are:
Children in direct contact with infected people.
Children inhale and swallow secretions and saliva of sick people when eating, drinking, coughing, sneezing, or talking.
Children come into direct contact with fluid from blisters, vesicles, and feces of the sick person.
Children holding toys and touching objects of children with hand, foot and mouth disease.
Children can be infected through the hands of caregivers.
Thus, in reality, children swimming in public pools are still at risk of contracting hand, foot and mouth disease if there is a source of infection. In swimming pools, the water environment is often mixed with a disinfectant solution, but it is still difficult to ensure that all harmful bacteria are killed.
If a child contracts hand, foot and mouth disease while exercising or swimming, the blisters on the skin can burst, peel off and spread the disease into the pool water or on slides, handrails, seats, locker room door handles, etc. In addition, there is also a source of infection from caregivers of children with hand, foot and mouth disease if they have close contact, shake hands, etc. Therefore, hand, foot and mouth disease can occur.
How many days does hand, foot and mouth disease incubate?
How many days will it take for a child to show signs of hand, foot and mouth disease if exposed to the source of infection? This is something that many parents are concerned about in order to monitor their children.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is identified in 4 stages:
- Incubation period, onset, full-blown disease and remission. Accordingly, the incubation period lasts 3 - 6 days after infection with the virus.
- During the onset period, the child will show the following symptoms:
Children have fever, fatigue, mild fever (37.5 - 38 degrees Celsius) or high fever (38 - 39 degrees Celsius).
Children with sore throat.
Children have mouth injuries and pain.
Children drool a lot.
Children with poor appetite.
This period lasts 1 - 2 days after the incubation period of hand, foot and mouth disease.
- Full-blown period: At this stage, the symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease are clear, usually starting 1-2 days after the onset of the disease. Children will have typical symptoms of the disease such as:
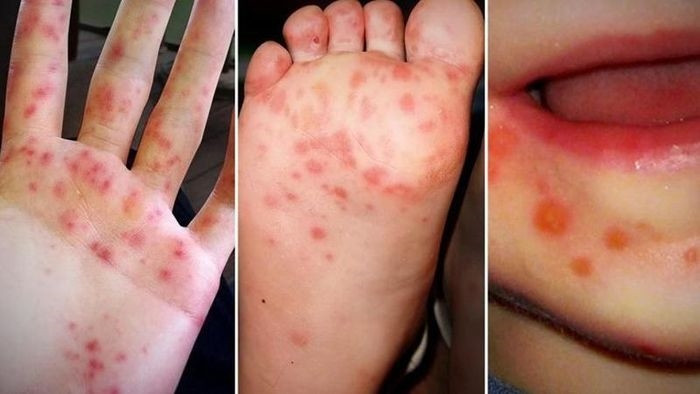
Children have blister-like rashes on the palms, soles, knees, and buttocks. The blisters are 2 - 10mm in diameter, gray, and oval.
The rash can be raised or hidden under the skin, feels rough to the touch, is painless, and does not itch.
Children with mouth ulcers: On the mucous membranes of the cheeks, gums and tongue of children, blisters with a diameter of 2 - 3 mm appear, very fragile. When broken, they form ulcers that cause pain when children eat, so children often cry.
Severe systemic signs: Perceptual disturbances, delirium, convulsions, vomiting, trembling hands and feet, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, cyanosis... The family needs to take the child to the hospital immediately.

Wash children's hands with soap regularly to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease.
What should parents do when their children have hand, foot and mouth disease?
Most children with mild hand, foot and mouth disease are monitored and cared for at home according to the following principles:
- Parents need to isolate properly: Sick children need to stay home from school and not play with friends for at least 10 days from the date of onset of the disease to prevent infection to other children. In homes with many children living together, they should be isolated completely. Sick children should be encouraged not to play with healthy children while they are sick. It is necessary to closely monitor the daily activities of sick children.
- Sick children and caregivers should wear medical masks. After contact, wash hands with soap and clean water immediately. Encourage children to wash their hands thoroughly and properly with soap under running water to prevent re-infection through hand-to-mouth contact. Sick children's clothes and diapers should be thoroughly disinfected with boiling water before being washed with soap.
- Personal items, cups, spoons, bowls... should be cleaned with boiling water and used separately. Create a clean and safe living environment to help children become healthier.
- Children need to eat scientifically, supplement with plenty of water, especially fruit juices containing many vitamins. The daily diet needs to ensure adequate nutrition. For breastfed children, it is necessary to increase breastfeeding times during the day. Children should avoid foods that can cause pain and damage to the mouth such as hot and thick foods.
Currently, there is no specific treatment for hand, foot and mouth disease, mainly symptomatic treatment including: Oral pain relievers and fever reducers by wiping the body with warm water, using Paracetamol fever reducer (dose 10 - 15mg/kg/time, each time 4 - 6 hours apart), can combine with Ibuprofen if the fever does not go down when prescribed by doctors. Absolutely do not use Aspirin to reduce fever and pain for children.
Take your child to the hospital immediately if you see any of the following symptoms:
Children have a high fever of 39 degrees Celsius that does not go down after actively reducing the fever.
The child was startled, panicked and bewildered.
Children show signs of shaking hands and feet (when giving toys to children to hold), weak limbs, and unsteady walking.
Children roll their eyes abnormally, vomit a lot, cry (cannot be comforted), have convulsions, have difficulty breathing...
According to Health and Life