According to the Ministry of Health, most cases of hand, foot and mouth disease are mild. However, in some cases, the disease can become severe and cause dangerous complications.
Increasing rate of hand, foot and mouth disease cases positive for Enterovirus 71 virus
According to the Ministry of Health, according to the report of the infectious disease surveillance system, in the first 5 months of 2023, the whole country recorded 8,995 cases of hand, foot and mouth disease in 63 provinces and cities, including 03 deaths in Dak Lak, Kien Giang, Long An. Compared to the same period in 2022 (12,649/1), the number of cases decreased by 28%, the number of deaths increased by 02 cases. The highest recorded cases were in the South (6,204/2), the North (2,007/0), the Central region 316/0), the Central Highlands (130/1)
Compared to the average of the past 5 years, the number of cases has not shown signs of a sudden increase, however, the number of cases in recent weeks has tended to increase rapidly and 3 deaths were recorded in May 2023.
Hand, foot and mouth disease cases are mainly found in boys (60%), girls account for 40% of the total number of cases. The majority of cases are in children under 10 years old (98.5%), of which the most common are in the 1-5 year old group, children attending nursery and kindergarten (84%) and under 1 year old (18%).
According to the Ministry of Health, most cases of hand, foot and mouth disease are mild. However, in some cases, the disease can progress severely and cause dangerous complications such as encephalitis - meningitis, myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema leading to death, so it needs to be detected early and treated promptly.
The results of microbiological surveillance of the pathogens causing hand, foot and mouth disease in 2023 recorded an increase in the proportion of cases positive for Enterovirus 71 (EV71) in the total number of samples tested, from 5.9% in week 14 of 2023 to 19.2% in week 20 of 2023. The emergence of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) has the potential to cause severe illness in some cases.
The Ministry of Health said that hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by viruses in the intestinal group, including Coxsackie, Echo and other intestinal viruses, of which the most common are intestinal virus type 71 (EV71) and Coxsackie A16.
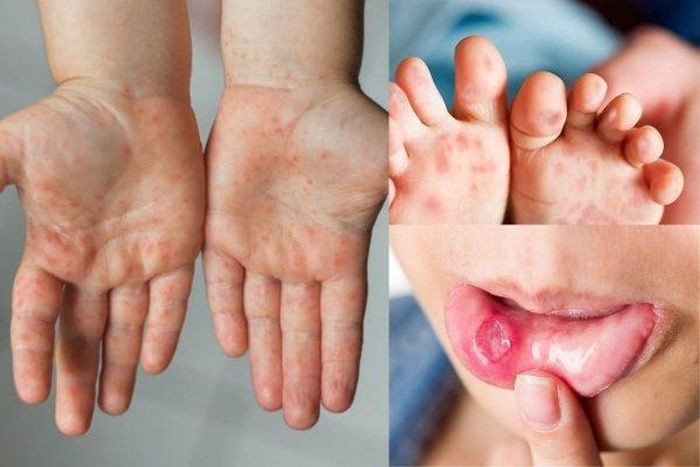
The disease is common in young children with typical symptoms of fever, sore throat, oral mucosal lesions and skin lesions mainly in the form of blisters often seen on the palms, soles, knees, and buttocks.
According to the Ministry of Health, most cases are mild. However, in some cases, the disease can progress severely and cause dangerous complications such as encephalitis - meningitis, myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema leading to death, so it needs to be detected early and treated promptly. The disease occurs year-round and is transmitted through the digestive tract, caused by poor personal hygiene, poor environmental hygiene, especially hygiene skills for children, and not washing hands with soap regularly.
In Vietnam, hand, foot and mouth disease is endemic and occurs in almost all 63 provinces and cities, often peaking in September - November every year, especially at the beginning of the new school year.
Strengthening hand, foot and mouth disease prevention on all 'fronts': Communication, community recommendations, treatment drugs, close monitoring of patients
The Ministry of Health said that in the past time, the Ministry has had many activities to lead, direct and urge the prevention of hand, foot and mouth disease. The Ministry of Health issued an Official Dispatch to the People's Committees of provinces and cities on strengthening the prevention of hand, foot and mouth disease; the Department of Preventive Medicine issued an Official Dispatch to the Department of Health of provinces and cities on strengthening the prevention of summer diseases, including hand, foot and mouth disease; the Department of Drug Administration also issued a document informing about the situation of treatment drugs, saying that it is expected that in July, Phenobarbital will be imported to treat hand, foot and mouth disease to Vietnam. Regarding drugs containing Immunoglobulin, there are currently 13 drugs containing Immunoglobulin that have been granted a valid circulation registration certificate in Vietnam.
Most recently, to minimize the number of deaths due to hand, foot and mouth disease, Deputy Minister of Health Tran Van Thuan signed and issued a document to the Department of Health of provinces and centrally run cities; hospitals under the Ministry of Health; health departments of ministries and branches on strengthening the treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease.
Accordingly, the Ministry of Health requires units to implement measures such as: Planning and implementing plans to prevent and control hand, foot and mouth disease in the area. Checking and evaluating human resources, facilities, medical equipment, drugs, chemicals and medical supplies at affiliated medical examination and treatment facilities to ensure readiness to receive and treat hand, foot and mouth disease.
Strengthen the monitoring of inpatients with hand, foot and mouth disease at medical examination and treatment facilities, especially during holidays and weekends, to promptly detect and treat when the disease worsens. Record complete and detailed medical records. Detect early, organize consultations and promptly refer patients when they have unusual developments.
At the same time, direct, inspect and supervise medical examination and treatment facilities to admit and treat patients according to the Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease issued together with Decision No. 1003/QD-BYT dated March 30, 2012 of the Minister of Health and refer to the professional contents in the Handbook for diagnosis and treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease in children of the Ministry of Health.
Strengthen infection prevention measures in hospitals, classify treatment routes, organize screening, classify outpatients and inpatients according to the hand, foot and mouth disease treatment flowchart and strengthen resources for hand, foot and mouth disease resuscitation units at the provincial level.
For hospitals such as: Central Hospital for Tropical Diseases, Central Children's Hospital, Hue Central General Hospital, Children's Hospital 1, Children's Hospital 2, Ho Chi Minh City Children's Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City Tropical Diseases Hospital, and provincial Tropical Diseases Hospitals, the Ministry of Health recommends reviewing conditions on human resources, facilities, medical equipment, drugs, chemicals and medical supplies at hand, foot and mouth disease treatment units to receive severe cases transferred from medical examination and treatment facilities in the province and other provinces.
The Ministry of Health said that it will continue to closely monitor the hand, foot and mouth disease situation, especially in provinces with increasing cases, and implement local disease prevention activities. It will maintain communication and advise the community on disease prevention and control through mass media...
6 recommendations to prevent hand, foot and mouth disease you need to know
To actively prevent and minimize the impact of hand, foot and mouth disease on health, especially children, the Department of Preventive Medicine, Ministry of Health strongly recommends that people proactively implement the following disease prevention measures:
1. Personal hygiene
Wash hands regularly with soap under running water many times a day (both adults and children), especially before preparing food, before eating/feeding children, before holding children, after using the toilet, after changing diapers and cleaning children.
2. Food hygiene:
Food for children must ensure adequate nutrition; cooked food and water; eating and drinking utensils must be washed thoroughly before use (preferably soaked in boiling water); use clean water in daily activities; do not feed children; do not let children eat with their hands, suck their fingers, or suck on toys; do not let children share napkins, handkerchiefs, eating and drinking utensils such as cups, bowls, plates, spoons, and toys that have not been sterilized.
3. Clean toys and living areas
Households, kindergartens, and home childcare providers need to regularly clean surfaces and objects that are in daily contact such as toys, school supplies, doorknobs, stair handrails, table/chair surfaces, and floors with soap or common detergents.
4. Collect and dispose of children's waste
Use hygienic toilets, children's feces and waste must be collected, treated and dumped into hygienic toilets.
5. Early detection monitoring
Children must be regularly monitored for their health to promptly detect, isolate, and treat cases of illness, avoiding the spread of disease to other children.
6. Isolate and treat promptly when the disease occurs
Nursery schools, kindergartens, child care groups and households with children under 6 years old need to proactively monitor the health of children to promptly detect and immediately take them to medical facilities for timely treatment. Sick children must be isolated for at least 10 days from the onset of the disease, not allowing children showing symptoms of the disease to attend class or play with other children. and immediately take the children to medical facilities for examination and treatment.
According to Health and Life