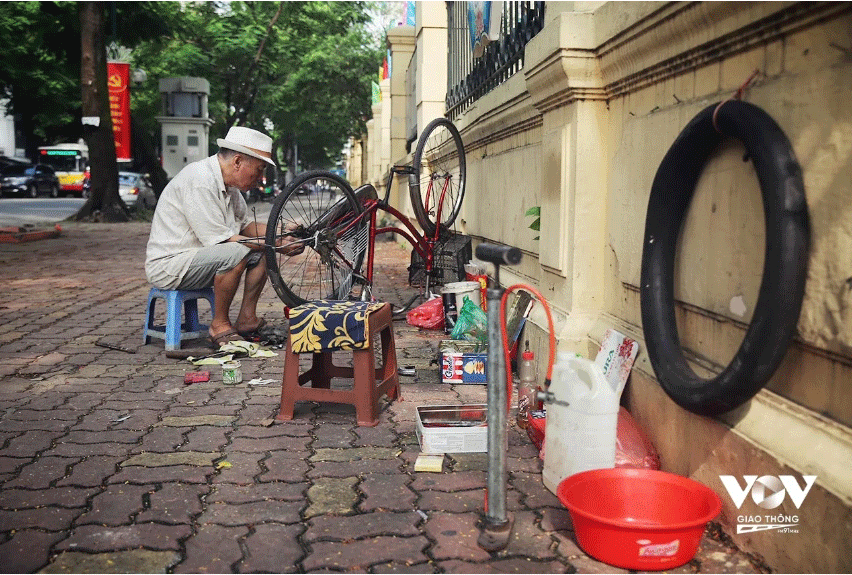
Submit a comment
Vietnam has entered the “aging” phase of its population since 2011 and is one of the countries with the fastest aging rate. The number of elderly people increases, the pressure on social security increases, how can they have a stable income in an expensive urban area?
Ms. Luong Thi Sau, 65 years old, from Kien Xuong, Thai Binh, has been in Hanoi to look after her grandchildren for 2 years now. She takes advantage of her time to do many jobs to earn an additional income of about 4 million VND/month to help her children:
"I do everything, I do whatever people hire me to do: washing dishes, cleaning by the hour, etc. When there are many customers, I serve, when there are no customers, I wash dishes. I go from 2-3am until 9-10pm, when I finish washing dishes, I go home. Last year, when I had work, I made more than 40 million, but this year I don't have steady work. My health is not tired, but my hands are numb."
According to statistics, in Vietnam, the number of people over 65 years old is about 11.4 million, but only 1/3 of them receive monthly pensions and social benefits. About 70% of elderly Vietnamese people live in rural areas and work in agriculture.
In urban areas, there are no more fields, many elderly people without pensions have to do all kinds of jobs: motorbike taxi, selling drinks, domestic help, etc. to have more money to live:
"Doing this is first of all ineffective, secondly it is hard work, rain or shine. A hundred bucks a day, plus gas and other expenses, it's not worth it. I really want to find a stable job but the situation is not as I wish."
"At this age, I don't know how to make a living anymore. Now I just hope that my superiors will create conditions for the people who don't have salaries and whose fields have all been confiscated."
Mr. Le Quang Trung, former Deputy Director in charge of the Department of Employment, Ministry of Labor, War Invalids and Social Affairs, assessed that employment for the elderly, especially in urban areas, is an urgent issue in the context that Vietnam is among the 10 countries with a rapidly aging population.
Solving employment for the elderly is like "killing many birds with one stone", ensuring social security, helping the elderly maintain both physical and mental health, and contributing to reducing the national human resource shortage.
According to the Labor Code and the Law on Employment, workers are Vietnamese citizens aged 15 and over, with no upper age limit, as long as they are capable of working and have a need to work. The State has a policy, but the implementation has not really received attention, leading to the elderly labor force with knowledge, experience, and responsibility being forgotten as a "treasure".
Mr. Le Quang Trung said: "We have not had any moves to change social awareness; there is no job exchange for the elderly; and we have not provided information about the needs of the elderly in the working process.
We do not have a support package for the elderly, employers do not hire the elderly; we do not organize vocational training, career transition for the elderly. For those starting a business, we also do not have training programs, support, and loan policies that the elderly have not accessed.
For urban freelance workers, they lack many things: lack of knowledge, information, and protection.

Agreeing with this view, Associate Professor, Dr. Cao Van Sam, Chairman of the Advisory Board, Institute for Training and Human Resources Development, senior expert on training and employment, said that in addition to Decision 1956 of the Prime Minister, some localities or associations also have short-term training projects, improving knowledge, skills, career transition, or even starting a business for the elderly.
However, the implementation is difficult in all three aspects: employment policy; career guidance, training, recruitment, career transition; and loans. Therefore, many synchronous solutions are needed to avoid the prospect that Vietnam may lack labor in the next 20 years as some forecasts:
"First, create a supply-demand labor market for elderly workers. Strengthen communication work, remove psychological barriers of inferiority when you are old. Third, strengthen career guidance, training and capital solutions.
Promoting models, for example, establishing a production development fund for the elderly with contributions from members; or using retired human resources to continue contributing to factories and enterprises. In urban environments, we need to equip them with more digital transformation skills, integration and adaptation skills.
Elderly intellectuals in the fields of education and health; other professions such as sales, security, housekeeping, nannying, insurance work, etc. can use short-term labor, on a case-by-case basis. The country must also have a strategy to adapt to an aging population soon."
Also emphasizing the improvement of the legal system on labor, employment and other laws related to the elderly, along with specific support programs, Mr. Le Quang Trung, former Deputy Director in charge of the Department of Employment, cited the experiences of some developed countries that Vietnam can learn from.
For example, Korea has a “second act of life” program that supports workers from the time they are still working and are about to enter their senior years. This program spends billions of dollars each year to provide information, advice, and training; has policies to support businesses in hiring senior workers; supports workers in lifelong learning and career transition; and provides both capital and knowledge if seniors want to start a business.

Society has long held the notion that the elderly need to rest and are not the subject of vocational training. Therefore, policies and regimes for elderly workers are still lacking, although many people still have the ability and desire to work and contribute.
In the context of improved health care and increased life expectancy, the issue of suitable employment for the elderly needs to be recognized soon with a positive approach from labor and employment policies.
According to VOV