Otitis media with effusion is a type of chronic, recurrent, closed eardrum otitis media. This disease is common in children and is also one of the causes that affect children's language development.
Characteristics of otitis media with effusion
People with otitis media with effusion often have the following symptoms:
Chronic effusion in the middle ear.
Patients with pure conductive hearing loss, sometimes mild, sometimes severe. Hearing loss often increases as the disease worsens.
Recurrent inflammation weakens the eardrum due to destruction of the collagen layer of the eardrum, the eardrum gradually softens, with negative pressure in the middle ear, the eardrum is pulled inward, gradually the eardrum sticks to the concave and convex areas of the ear canal and sticks to the inner wall of the ear canal, the ossicles are fixed.
If left untreated, otitis media with effusion can cause many serious consequences such as hearing loss. In young children, it will affect language development, communication, and learning.
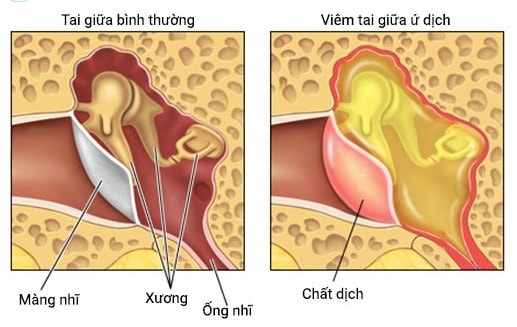
Otitis media with effusion is a chronic, recurrent type of otitis media with closed tympanic membrane.
The cause of otitis media with effusion is adenoiditis, mainly due to adenoid hypertrophy blocking and compressing the Eustachian tube opening, causing Eustachian tube obstruction. Partly due to pus from adenoiditis accumulating in the Eustachian tube opening, causing Eustachian tube obstruction and otitis media. Otitis media with effusion can heal on its own but is prone to recurrence.
Treatment of otitis media with effusion
The goal of treatment is to ventilate the middle ear, restore hearing to the patient, treat the cause, and prevent recurrence.
Doctors often prescribe medical treatment in the early stages of the disease and in cases where the patient does not agree to surgical treatment. Mainly antibiotics, expectorants, and anti-allergy drugs are used.
Surgical indications include incision of the tympanic membrane and placement of a ventilation tube to drain fluid in the tympanic cavity to help improve the child's hearing and prevent recurrence by providing ventilation to the middle ear.
Otitis media with effusion can become infected and cause complications such as chronic suppurative otitis media, perforated eardrum, and prolonged effusion. Illustration photo
Doctor's advice
Otitis media with effusion can have different developments, usually can be self-healing from 10-20 days. Or after being treated properly, hearing ability is restored. However, in some cases, despite being treated properly according to the regimen, otitis media with effusion still recurs.
Otitis media with effusion can become infected and cause complications such as chronic otitis media with effusion, perforated eardrum, and prolonged effusion.
- Because otitis media with effusion is often overlooked because the symptoms are silent, parents should take their children to see an ENT specialist if they often put their hands on their ears, feel uncomfortable, or have slow reactions to surrounding sounds.
- When the weather changes, parents need to keep their children warm, improve their resistance, and vaccinate them fully. Especially, when children have upper respiratory tract infections, they need to be treated thoroughly, not letting the disease last.
- Clean your ears properly, avoid getting water in your ears. Do not use hard objects to remove earwax, and do not share earwax removal tools.
- Otitis media with effusion is a dangerous disease for children, it causes hearing loss affecting language development, communication, learning, if not diagnosed and treated promptly, the disease will cause many dangerous complications and sequelae.
- Children should have regular ENT check-ups to detect and treat otitis media with effusion and ear problems early.
According to Health and Life